Third-Party and BYOD Remote Access
Providing contractors, partners, and other third-parties secure access to applications and resources is often handled as a special case, adding to network complexity and creating security risk. The right approach avoids overly-broad legacy VPN access and instead uses continuous authorization against a context of user and device trust to authorize access.The Problem
Today’s workforce is highly mobile and uses a mix of device types. Employees, partners, contractors, and third-parties alike need to access sensitive resources and applications utilizing corporate-managed and unmanaged personal (BYOD) devices.

Massive Security Gap
- Traditional VPNs enable overly-broad access to your network. A compromised VPN allows lateral movement across networks leading to massive exposure.
- Legacy VPNs rely on a one-time authorization approach with no ability to monitor abnormal activity to detect potential breaches.

Management Nightmare
- No centralized way to secure IaaS, on-premises, and SaaS applications based on security posture of users and devices result in operational complexity.
- Complex network-level policies to segment access, which have to be constantly updated to match dynamic user and application environments.

Bad User Experience
- Due to complexity in deployment, users experience performance delays and in many cases are unable to access applications due to VPN connectivity issues.
- IT admins find legacy VPNs are expensive to acquire, maintain, and upgrade.
Banyan Zero Trust Solution for Secure Resource Access
Increasingly mobile users – employees, partners, contractors, and 3rd party developers – need to access resources and applications utilizing personal devices which are typically unmanaged.
The changing nature of the people and devices that access sensitive resources and applications across distributed deployments models make legacy VPNs ill-suited to protect this environment.
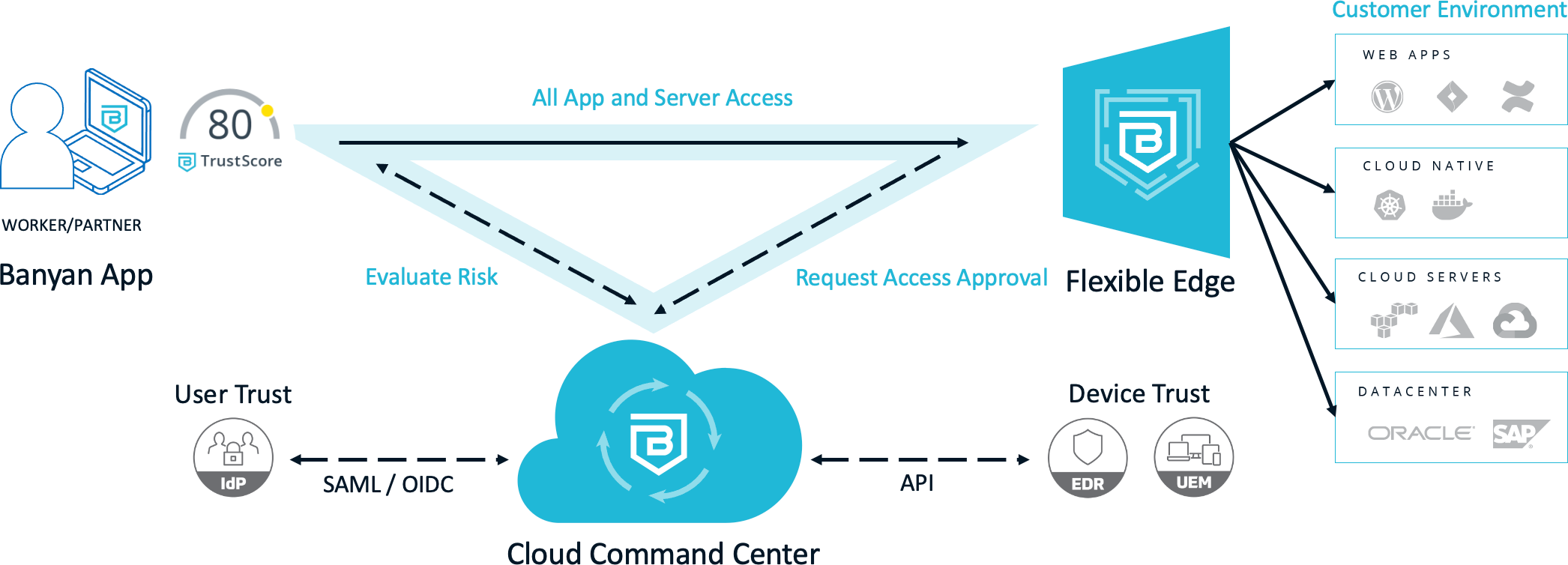
There is a better way to achieve Zero Trust Access to your resources and infrastructure without requiring a VPN and more importantly, dramatically reducing your vulnerability footprint. With Banyan, you define trust-based access policies that govern user access to hosts, servers, applications (including SaaS apps), and even APIs.
No other solution can provide this fine-grained control, all while offering an alternative to cumbersome centralized VPNs. Now, with Banyan Zero Trust Access you can achieve direct, secure, least-privileged access to your resources.
Banyan Security’s remote access solution is comprised of three core components that together deliver a complete Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solution. First, we offer Trust Scoring capability for quantification of user and device trust and related contextual factors. Next, we provide continuous authorization of access via our Cloud Command Center. And finally we offer real-time access enforcement based on the principle of least privilege.
Superior Security Posture
- Orders of magnitude attack surface reduction by delivering least privilege access based on quantified trust and continuous authorization
- Real-time enforcement of access policy on a per resource/application basis for complete end-to-end security

Comprehensive Solution
- Consistent user experience whether applications are deployed in IaaS, on-premises, or delivered via SaaS
- Support for all applications; Private, internal apps (DevOps – Jira/Jenkins/Confluence to SecOps – Splunk & Demisto, to admin consoles on VMware or AWS to SaaS applications like Workday)

Seamless End-User Experience
- Direct access to applications be they private cloud or SaaS deployments
- Simplified access policies tied to user, device, and application profiles for ease of management
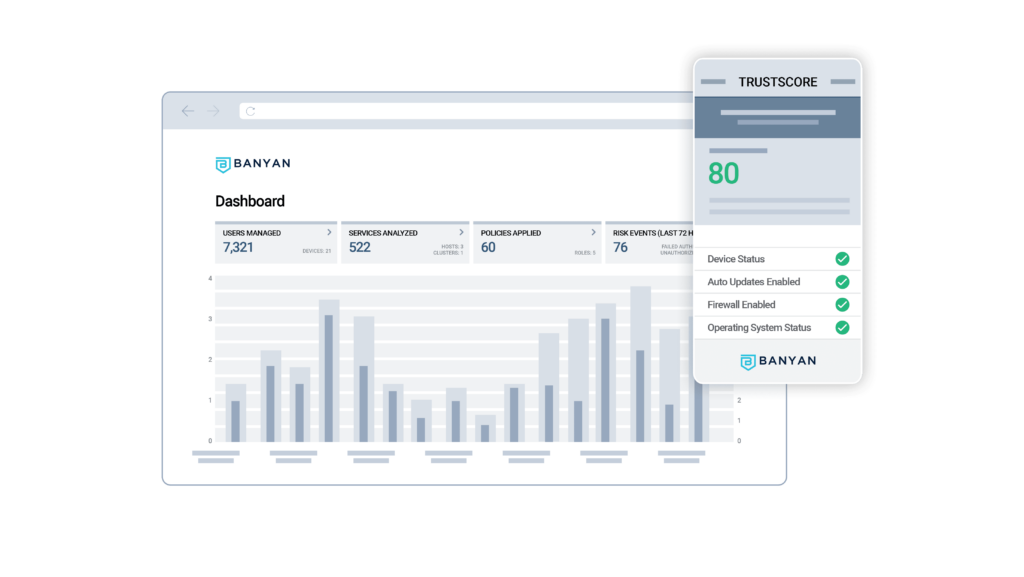
Key Features for Secure Application Access
- Real-time check of user and device security posture before granting access using employee-visible TrustScore
- Continuous authorization post-login to enable enforcement for events like the latest zero day detected by EDR tool resulting in immediate denial of access
- Leverage standard protocols (e.g., TLS, HTTPS, SSH) without reliance on any custom protocols
